The last-mile market has grown at around 16% per year in North America from 2021 to 2025, based on Technavio’s report. Online shopping’s popularity has a great impact on that, as customers now expect a faster and more reliable delivery experience.
But as this trend continues, ecommerce merchants have found themselves facing higher shipping costs, unplanned delays, and more return-to-sender cases. If this keeps up, it can hurt revenue and weaken customer trust.
In this article, we’ll walk you through everything about last-mile delivery: the types, the challenges, and, most importantly, how to solve these last-mile problems.
What Is Last-Mile Delivery?
Last-mile delivery is when the package moves from a local warehouse, sorting center, or delivery hub directly to the customer’s home or a dedicated drop-off/pick-up point. It’s also the “final phase” of the shipping process.
Before the package reaches the customer, it goes through these three stages:
- First-mile delivery happens when the product is sent from the seller to the first warehouse or fulfillment center.
- Middle-mile delivery covers all that happens in between. It’s when the package moves between warehouses, distribution centers, and sorting hubs in different regions to bring it closer to the “delivery area”.
- Last-mile delivery is the final stretch handled by a local carrier who completes the delivery.
Each stage has a special role in moving orders forward. But the last mile is often where most delivery challenges start to appear for ecommerce businesses and logistics teams.
The High Cost and Complexity of the Last Mile Delivery
50Folds’ report showed that last-mile delivery accounts for 53% of total shipping costs. It’s no secret that it’s the most expensive part of the shipping process.
But why is that the case?
Unlike bulk shipping, last-mile delivery is more complex. Drivers deliver to just a few homes per route, and urban traffic makes each stop challenging. Busy streets, traffic jams, and narrow lanes further increase delivery time and cost.
And companies need to bring in more drivers to handle last-mile deliveries. DispatchTrack’s last-mile analysis showed that labor costs are the biggest expense and make up 50-60% of total delivery costs.
Last-mile costs increase even more because of failed delivery attempts that require redelivery and may add fees from returns and reverse logistics.
Why Does Last-Mile Delivery Matter?
Last-mile delivery is the most important part of the customer post-purchase journey. It has a direct impact on customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
However, do you know what customers expect more for last-mile delivery? Free, fast, and transparent delivery.
You may already know how to choose cheaper and faster shipping services, but are you doing your best when it comes to last-mile tracking?
Customers want to see exactly where their packages are and when they will arrive. Without this visibility, they can get anxious and send multiple WISMO messages to your support team. That means you need more staff to handle these inquiries, which increases your costs.
By providing a smooth and transparent delivery experience, you can strengthen customer trust in your brand and turn them into repeat buyers.

How Does Last-Mile Delivery Work?
Last-mile delivery moves your customer’s order from the warehouse straight to their door.
Step 1: Order Processing
When an order is placed, it will be sent to the nearest fulfillment center to confirm stock, and a tracking number will be created. Both the merchant and the customer can use it to track the shipment.
Step 2: Transportation Hub Sorting
Your package goes through several facilities before reaching the local transportation hub. Once it’s there, it gets scanned and sorted by ZIP code (or routes).
Step 3: Dispatch & Route Assignment
The routing software collects all delivery details (addresses, package size and weight, etc.) and maps out the most efficient delivery paths.
After routes are assigned to drivers, the packages officially enter the last-mile delivery stage.
Step 4: Scanning & Loading
Each package is scanned before loading into the van, and its tracking status changes to “Out for Delivery”.
Once done, warehouse teams strategically load them (i.e., using last in, first out to match the delivery order), so the driver can access each package quickly at the final delivery destination.
Step 5: Delivery Completion
The driver arrives at the location, confirms the address, and completes the delivery.
Step 6: Proof of Delivery
If a signature is required, the driver collects it on a handheld device. If not, they usually take a delivery photo (for proof). This ends the last-mile delivery process.
Types of Last-Mile Delivery Services
The types of delivery services used in last-mile operations depend widely on the product and the level of speed or convenience customers expect. They can range from basic, low-cost options to faster or more specialized services.
Most retailers use a mix of these to balance cost and customer satisfaction. Here are some common types of last-mile delivery services:
Standard & Deferred Delivery
Standard parcel delivery is the most common shipping option in ecommerce. Orders usually arrive within two to seven business days through postal and parcel carriers. It is mainly used for non-urgent online purchases (clothing, phone accessories, etc.) because it keeps shipping costs low while still meeting basic delivery expectations.
Some sellers also offer deferred delivery for a more affordable option, where customers agree to receive their order at a later date instead of the earliest possible time.
These services are more for threshold deliveries, where packages are left at the doorstep, mailbox, or a building’s receiving area. They usually do not require a signature for confirmation.
Same-Day & On-Demand Delivery
These two “instant” models have become common in modern ecommerce. And that’s because food apps and similar services normalized faster delivery experiences.
Same-day delivery runs on a set schedule and uses a cutoff time (whether 12 noon or 2:00 PM) to decide which orders make it into the day’s planned route.
On-demand is more immediate, and one driver is assigned right after checkout. There’s no batch shipping or fixed route, so the order moves as soon as it’s picked up.
Both options rely on local couriers or gig drivers, and they are more expensive compared to standard shipping.
White Glove Delivery
Next is white glove delivery, which is a premium last-mile service for fragile, large, or bulky, and expensive items. Some examples are furniture, appliances, and electronics.
In this setup, trained delivery teams bring the item inside the home, then place and assemble it in the customer’s “room of choice”. Most teams also offer to clean up the packaging and even remove the older item afterward.
It’s a high-touch service and is more ideal for high-ticket items where customers spend more for a personalized setup experience beyond door delivery.
Smart Lockers
Smart lockers are secure pickup spots where packages get delivered. Customers can claim their orders from these lockers with a QR code, PIN, or mobile app to grab their orders whenever they want.
This delivery option provides customers a window (usually 2-7 days) to collect their package. If they fail to do so, the package goes back to the sender.
Smart lockers are great for stopping package theft and missed deliveries since customers don’t have to wait around at home. Plus, most of them are accessible 24/7.
PUDO (Pick-Up/Drop-Off)
PUDO points have some similarities with smart lockers. But PUDO points often rely on staffed locations and store hours instead of being fully automated like smart lockers.
These PUDO points include retail partner locations, carrier centers, and community hubs in public spaces like shopping centers.
If the customer chooses this, they need to wait for a pickup notification. After receiving the code, they can visit the location, present their ID for verification, and collect their package.
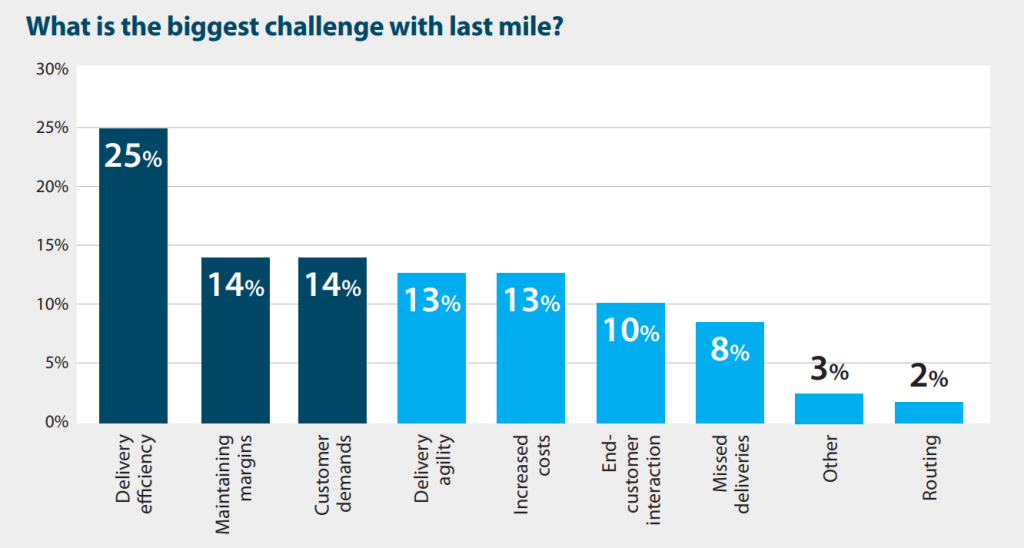
What Is the Last-Mile Problem?
Delivery efficiency is the biggest challenge for last-mile providers. It is further complicated by traffic, rural reach, and failed deliveries, which together increase operational costs.
Dealing with Traffic Congestion
Urban traffic congestion can seriously slow down last-mile delivery and throw drivers off schedule. Besides delays, it burns more excess fuel, as stop-and-go movement uses more than steady driving.
Unpredictable road conditions also create another problem. Construction, emergency repairs, rallies, or flooding can block key roads and force drivers to reroute. And since these events can occur at any time, they often cause delivery delays that are hard to predict.
Addressing Rural Areas Reach
In rural areas, each stop is far from the next. Since there aren’t many deliveries in one route, the cost per package is higher.
Reaching some addresses can take even longer, too. Certain locations don’t have clear house numbers, and some sit behind private roads or narrow gravel paths. When that happens, delivery vehicles often need to turn back or take a different route.
This rural condition is why many carriers add surcharges for remote areas. They account for the extra time, fuel, and resources required to complete these runs.
Solving the Failed Deliveries Problem
Failed deliveries often happen because the customer isn’t home. Other common causes include incorrect or incomplete addresses, access restrictions, and closed businesses (for commercial delivery).
Since porch piracy has become so common nowadays, carriers have to hold the packages instead of leaving them at the doorstep, even if it means more delivery attempts.
The courier needs to reschedule the route, and if the schedule is full, customers may have to wait several days for their delivery. Some couriers may also charge additional fees for a second delivery or storage, or they might return the package to the sender.
Even worse, the package could get lost if it’s misplaced during delivery or returned incorrectly, and no one would know where it went. And while the courier might cover the cost, you could end up losing a loyal customer over the experience. This is why avoiding failed delivery matters.
Managing High Operational Costs
By now, you can see how hard it is to balance delivery efficiency and costs. Fuel, labor, and vehicle maintenance rise fast when drivers cover long distances and individual stops. Missed deliveries and extra handling also add to the already expensive process.
But you can lower operational costs with better delivery planning. It can be optimizing delivery routes to reduce fuel and labor costs or tracking package status in real time during shipping. All of these strategies can help improve last-mile delivery performance.
If last-mile delivery makes up most of your costs, it’s a good idea to start optimizing it today.
You may be interested in:
How to Solve Last-Mile Delivery Challenges
Best Last-Mile Delivery Software Solutions in 2026
How Technology Solves Last-Mile Delivery Problems
Route optimization software, real-time tracking systems, electric vehicles, and automated fulfillment centers all help reduce the operational costs and delivery inefficiencies we discussed earlier. Here’s how these technologies solve last-mile delivery problems:
Route Optimization Software
Route optimization software helps achieve timely and accurate deliveries by reducing inefficient routing. That’s through calculating real drive times, traffic flow, delivery windows, and vehicle limits. It processes all of this in seconds and arranges the stops in the best order for the day’s route.
Because the stops are organized, drivers can avoid detours and backtracking. It can reduce extra mileage, fuel use, and long hours that cause driver fatigue.
It also offers dynamic routing that continuously collects live data. If the weather changes, traffic builds, or a road closes in real time, the software can reorder stops or reroute the driver to stay as close to the estimated time of arrival (ETA).
Real-Time Tracking System
A real-time tracking system keeps both you and your customers updated on the latest status and location of packages.
Customers receive automatic updates whenever their orders are shipped, in transit, out for delivery, or reach any other important milestone. Notifications can be sent via email, SMS, or any social messaging platform you’ve set up, and the process is fully automated.
Some tracking platforms also provide an order tracking page, allowing customers to check their orders themselves. You can even customize the page with your brand assets, such as your logo and brand colors.
A tracking system also offers another big advantage. By consolidating all tracking information from every carrier in one place, it provides valuable logistics insights to help improve shipping performance. You can monitor delivery success rates, compare transit times across different carriers on the same route, and spot the routes where delivery issues happen most often.
Electric Delivery Vehicles
A zero-emission delivery report shows that more than 37,000 zero-emission cargo vans are now used in the U.S. Heavy-duty electric truck adoption is also rising (from about 200 units in 2021 to 1,600 in 2023).
Electric vehicles (EVs) hugely reduce emissions because they do not burn fuel during deliveries and remain efficient in stop-and-go traffic. They also recover energy through regenerative braking, which works well for short city routes with frequent stops. Over time, it’ll lead to lower energy use per route and lower carbon output.
Another advantage is their “quiet motor.” EVs create very little noise and make it possible to deliver early-morning or late-night without disturbing neighborhoods. So, drivers can avoid rush hour and drop off packages faster.
Now that customers are becoming more eco-conscious, they prefer buying from businesses that support green shipping options. It’s important to be part of this movement.
Automated Fulfillment Centers
Automated Fulfillment Centers are transforming last-mile delivery.
Inside these facilities, automation handles most of the work. Robots move inventory, scanners keep track of every step, and orders move through picking and sorting much faster than with traditional manual operations.
If you run your own warehouse, labor costs are undoubtedly one of your biggest headaches. You might prefer hiring temporary workers since they’re cheaper, but they are often unreliable, and high turnover further reduces efficiency. Automation helps solve these challenges.
Key Trends Shaping Last-Mile Delivery in 2026
The last-mile delivery industry has been changing quickly to keep up with customer expectations and ecommerce growth.
Customers look for faster, cheaper, and more sustainable delivery options, and that pushes logistics providers and merchants to adjust how they operate. So, here are three key trends shaping last-mile delivery in 2025:
AI & Machine Learning Integration
AI and machine learning are moving beyond basic route planning into predictive logistics. These systems can now analyze past order volume, seasonality, and location data to prepare for future delivery demand.
For example, during Black Friday, it can learn from historical data to predict which areas will see the highest order volume. Based on these predictions, the system can allocate more drivers and other resources strategically, ensuring packages are delivered on time even during peak periods.
Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs)
Online shopping is now part of everyday life, and customers aren’t willing to wait days for their orders anymore. They want them as quickly as possible.
To satisfy customers, companies are moving warehouses closer to cities. But high urban rents often make it difficult to set up large fulfillment centers, so many merchants are turning to a clever solution: using the store’s back room or a dark store as a micro-fulfillment center.
These centers can be semi-automated or fully automated, which depends on the scale of the store.
Mirco-fulffilemnt centers allow customers to have their orders in hand within a few hours or stop by the store to pick them up whenever they like.
Autonomous Drones and Robots
Some logistics companies are now deploying drones for last-mile delivery. They can bypass traffic congestion, reach hard-to-access areas, and deliver small parcels quickly and efficiently.
Sidewalk robots are another food delivery option (for short distances). They use sensors and GPS to move on sidewalks and work best in campuses, business parks, and dense neighborhoods with predictable routes.
Even with the progress, these autonomous delivery vehicles still have limitations. Regulations are strict in many places, and some states restrict flights near private facilities.
One more factor is their technical capacity, since bad weather, uneven paths, and short battery life can interrupt their trips. And it’s expensive to maintain them.

Conclusion
That’s it for this article, and congratulations on finishing it!
Last-mile delivery has become one of the most important parts of the modern ecommerce workflow. It affects cost, customer experience, and distinguishes you from competitors during the post-purchase journey.
Staying competitive means keeping last-mile delivery organized, predictable, and centered on the customer. And investing in the right tools, technology, and delivery services can make that easier.
TrackingMore provides you with reliable, fast, and accurate last-mile visibility. You can track shipments across 1,500+ carriers on one dashboard just via CSV uploads or API integration. Our system can send shipping notifications to your customers automatically via email and SMS. By offering them complete transparency, you can expect fewer WISMO tickets and happy customers.
Ready to strengthen your last-mile performance? Get started with TrackingMore for free.
FAQs about Last-Mile Delivery
Last-mile delivery is expensive because it involves delivering individual packages to many separate addresses, often in congested urban areas. This increases labor, fuel, and time costs, and failed deliveries add extra trips and expenses.
Businesses can lower last-mile delivery costs by optimizing delivery routes. Sending real-time order updates also helps to avoid missed deliveries. Beyond these strategies, using electric vehicles can cut fuel consumption, and automated fulfillment centers can speed up delivery by bringing products closer to customers.
Last-mile delivery software handles route planning, real-time tracking, scheduling, and delivery confirmation. This software helps keep routes organized and communication clear, which makes the delivery process easier for both drivers and customers.
You can track last-mile delivery logistics through the carrier’s tracking page, app, or SMS updates. Shipment tracking platforms like TrackingMore offer real-time tracking status for 1,500+ carriers worldwide, so you can track all your shipments in one place.
Easton has 3 years of experience researching and writing about e-commerce and logistics. She enjoys sharing the latest industry trends and insights with readers.